Cell Nucleus - Commanding the Cell
The cell nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. If it happens in a cell, chances are thenucleus knows about it. The nucleus is not always in the center of the cell. It will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of all of the cytoplasm (cytosol). You probably won't find it near the edge of a cell because that might be a dangerous place for the nucleus to be. If you don't remember, the cytoplasm is the fluid that fills cells.
Life Before a Nucleus
Not all cells have a nucleus. Biology breaks cell types into eukaryotic(those with a defined nucleus) and prokaryotic (those with no defined nucleus). You may have heard of chromatin and DNA. You don't need a nucleus to have DNA. If you don't have a defined nucleus, your DNA is probably floating around the cell in a region called the nucleoid. A defined nucleus that holds the genetic code is an advanced feature in a cell.
Important Materials in the Envelope
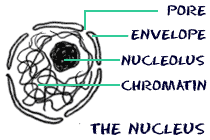 The things that make a eukaryotic cell are a defined nucleus and other organelles. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and all of its contents. The nuclear envelope is a membrane similar to the cell membrane around the whole cell. There are pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and nucleolus inside.
The things that make a eukaryotic cell are a defined nucleus and other organelles. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and all of its contents. The nuclear envelope is a membrane similar to the cell membrane around the whole cell. There are pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and nucleolus inside. 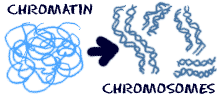 When the cell is in a resting state there is something called chromatin in the nucleus.Chromatin is made of DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. DNA and RNA are the nucleic acids inside of the cell. When the cell is going todivide, the chromatin becomes very compact. It condenses. When the chromatin comes together, you can see the chromosomes. You will also find the nucleolus inside of the nucleus. When you look through a microscope, it looks like a nucleus inside of the nucleus. It is made of RNA and protein. It does not have much DNA at all.
When the cell is in a resting state there is something called chromatin in the nucleus.Chromatin is made of DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. DNA and RNA are the nucleic acids inside of the cell. When the cell is going todivide, the chromatin becomes very compact. It condenses. When the chromatin comes together, you can see the chromosomes. You will also find the nucleolus inside of the nucleus. When you look through a microscope, it looks like a nucleus inside of the nucleus. It is made of RNA and protein. It does not have much DNA at all.
 The things that make a eukaryotic cell are a defined nucleus and other organelles. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and all of its contents. The nuclear envelope is a membrane similar to the cell membrane around the whole cell. There are pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and nucleolus inside.
The things that make a eukaryotic cell are a defined nucleus and other organelles. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and all of its contents. The nuclear envelope is a membrane similar to the cell membrane around the whole cell. There are pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and nucleolus inside.  When the cell is in a resting state there is something called chromatin in the nucleus.Chromatin is made of DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. DNA and RNA are the nucleic acids inside of the cell. When the cell is going todivide, the chromatin becomes very compact. It condenses. When the chromatin comes together, you can see the chromosomes. You will also find the nucleolus inside of the nucleus. When you look through a microscope, it looks like a nucleus inside of the nucleus. It is made of RNA and protein. It does not have much DNA at all.
When the cell is in a resting state there is something called chromatin in the nucleus.Chromatin is made of DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. DNA and RNA are the nucleic acids inside of the cell. When the cell is going todivide, the chromatin becomes very compact. It condenses. When the chromatin comes together, you can see the chromosomes. You will also find the nucleolus inside of the nucleus. When you look through a microscope, it looks like a nucleus inside of the nucleus. It is made of RNA and protein. It does not have much DNA at all. 







0 comments:
Post a Comment